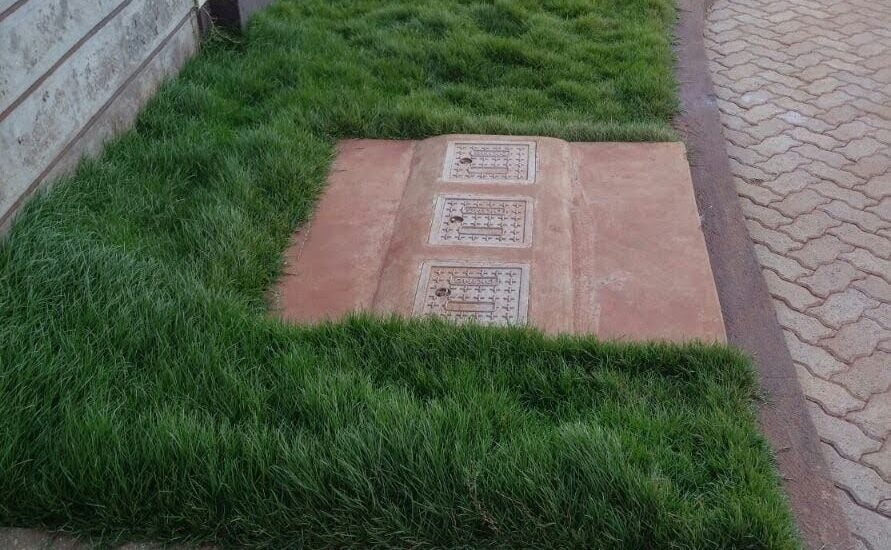
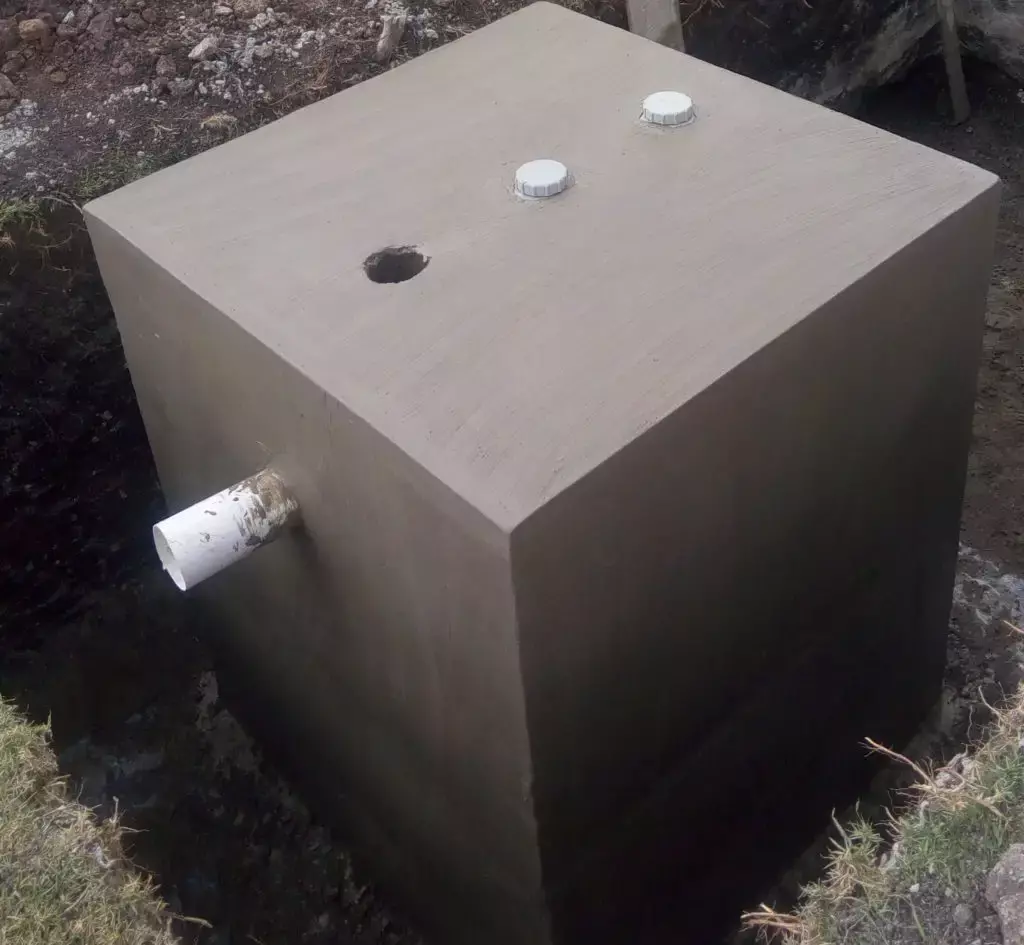
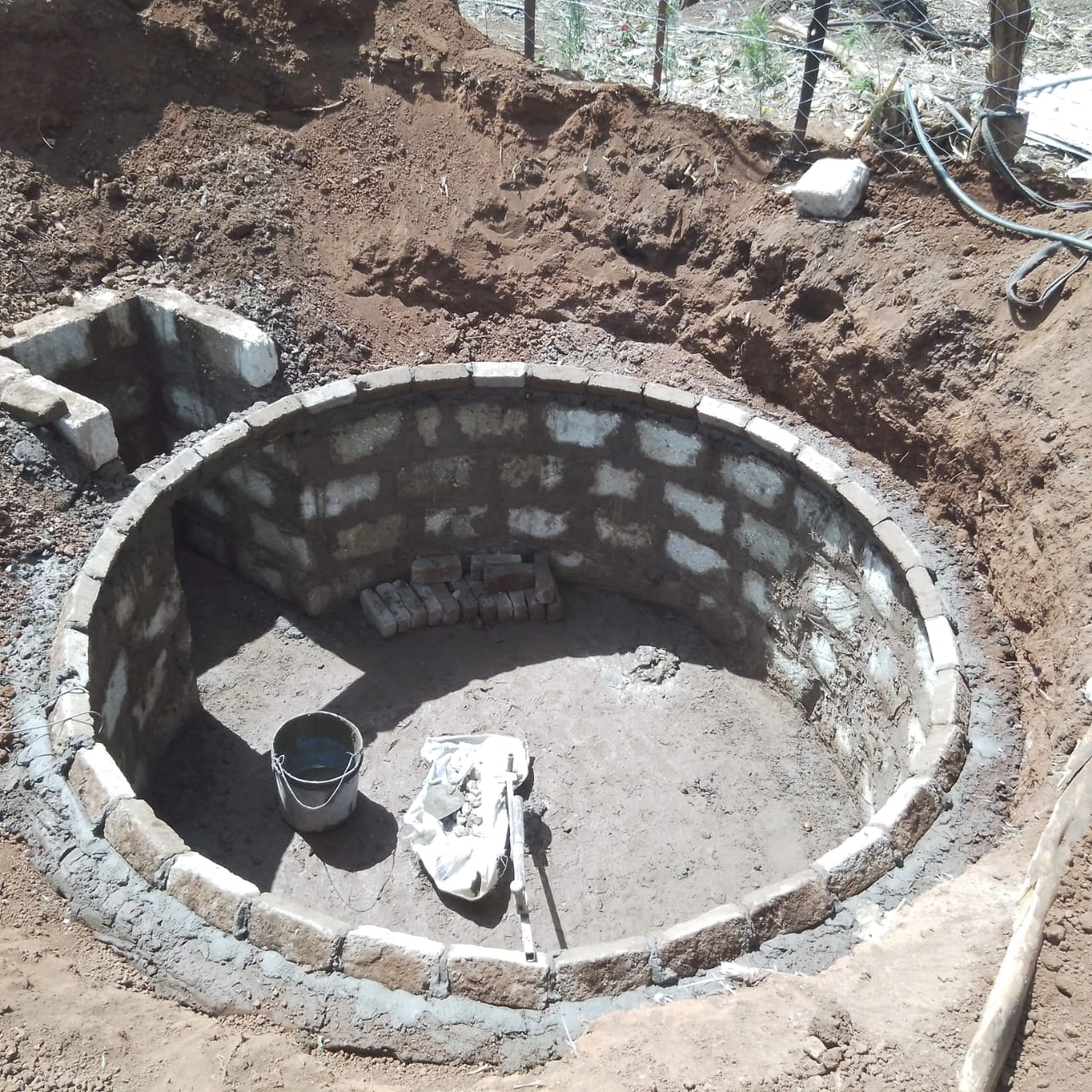
Bio Digesters have started becoming common in the Kenyan Market. They are the perfect way to deal with watste management especially in urban areas where the cost of waste management is high. Many households have to rely on the expensive services of an Exhauster.
With a Bio Digester, households can cut the cost of waste management by installing a Bio Digester in their premises. You can read about how Bio Digesters work here.
In this article, we will delve into how Bio Digester Bacteria work. These Bacteria help to digest waste inside the Bio Digester.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Bio digesters are an innovative solution for waste management and renewable energy production.
They use the process of anaerobic digestion to break down organic matter, producing biogas that can be used as a renewable energy source.
Bio digesters are becoming increasingly popular around the world, especially in rural areas where they can help address waste management challenges and provide a reliable source of energy.
Understanding Bio Digester Enzyme Bacteria
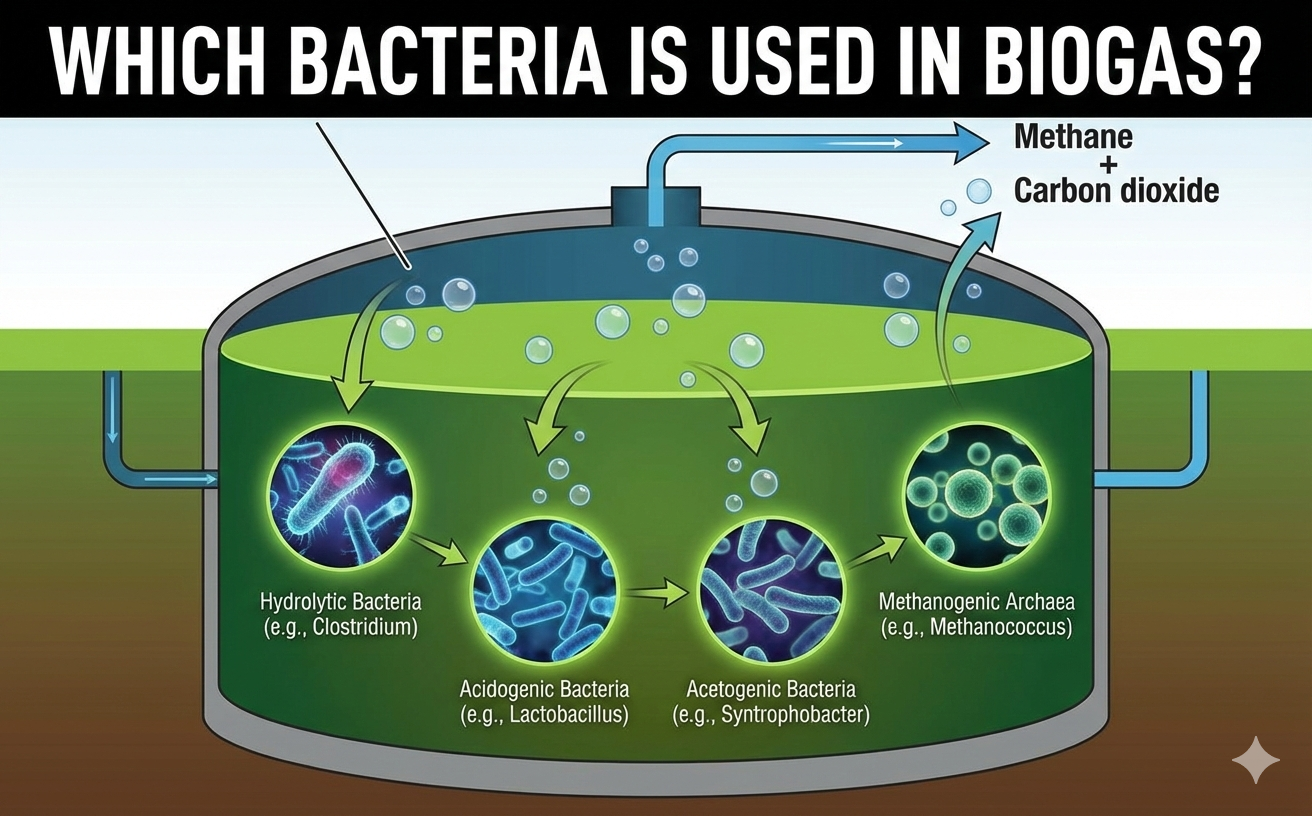
Bio digesters rely on the action of various types of bacteria, enzymes, and anaerobic bacteria to break down organic matter and produce biogas.
Anaerobic bacteria are bacteria that can survive in environments without oxygen.
They play a crucial role in bio digesters, where they break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas as a result.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms.
In bio digesters, enzymes help break down complex organic matter into simpler compounds that can be digested by the bacteria present in the system.
Different types of bacteria are involved in the process, including acid-forming bacteria, methane-forming bacteria, and others.
How Do Bio Digester Enzyme Bacteria Work?
Bio digesters work by creating an anaerobic environment that allows bacteria to break down organic matter.
The process starts with the introduction of organic waste into the digester, where it is mixed with water and other materials to create a slurry.
The bacteria in the system begin to break down the organic matter, releasing biogas as a byproduct.
The biogas produced in the system is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, and other gases. The biogas can then be extracted from the system and used as a renewable energy source.
In addition to bacteria and enzymes, the breakdown of organic matter in bio digesters is also influenced by other factors, such as temperature, pH level, nutrient balance, and organic loading rate.
These factors must be carefully controlled to ensure optimal conditions for the bacteria to thrive and produce biogas.
Factors Affecting Bio Digester Enzyme Bacteria
Temperature is one of the most important factors affecting the activity of anaerobic bacteria in bio digesters.
The bacteria require a warm environment to thrive and produce biogas.
pH level is a critical factor that affects the activity of enzymes and bacteria in bio digesters.
The pH level of the system must be maintained at around 7.0 to 7.5 to ensure optimal conditions for the bacteria to thrive.
Nutrient balance is also essential in bio digesters, as the bacteria require a specific balance of nutrients to survive and produce biogas.
The optimal balance of nutrients in the system is achieved by adding different types of waste materials, such as cow dung, poultry manure, and other organic waste.
Organic loading rate is another factor that can affect the performance of bio digesters.
Organic loading rate refers to the amount of organic waste added to the system each day.
If the organic loading rate is too high, it can lead to a buildup of solids in the system, which can inhibit the activity of bacteria and enzymes.
Advantages of Bio Digesters
Bio digesters offer a range of advantages over other forms of waste management and energy production.
Some of the key benefits of bio digesters include:
- Renewable energy source: Biogas produced in bio digesters is a renewable energy source that can be used for cooking, heating, and generating electricity.
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Bio digesters help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere during the decomposition of organic waste.
Reduced waste disposal costs: Bio digesters provide an effective solution for managing organic waste, which can be costly to dispose of using traditional methods.
Improved soil fertility: The slurry produced in bio digesters is rich in nutrients and can be used as a fertilizer for crops, improving soil fertility and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Improved sanitation: Bio digesters can help improve sanitation in areas where open defecation is common, by providing a safe and hygienic way to manage human waste.
Challenges of Bio Digesters
While bio digesters offer many benefits, there are also several challenges associated with their use. Some of the key challenges of bio digesters include:
Initial investment costs: Bio digesters can be expensive to set up and require ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
Technical expertise: Bio digesters require specialized technical expertise to design, build, and operate effectively.
Feedstock availability: The availability and quality of feedstock can vary depending on the location and season, which can impact the performance of bio digesters.
Regulatory challenges: Bio digesters may be subject to regulations and permits, which can be time-consuming and costly to obtain.
Conclusion
Bio digesters are a promising solution for waste management and renewable energy production.
They rely on the action of various types of bacteria, enzymes, and anaerobic bacteria to break down organic matter and produce biogas.
While bio digesters offer many benefits, they also face several challenges, including high initial investment costs and regulatory hurdles.
Despite these challenges, bio digesters have the potential to play a significant role in addressing waste management and energy production challenges around the world.
FAQs
- What types of waste can be used in bio digesters? Bio digesters can be used to break down a range of organic waste, including agricultural waste, food waste, and human and animal waste.
- What is the optimal temperature for bio digesters? The optimal temperature for bio digesters is around 37 to 40 degrees Celsius.
- What is the main byproduct of bio digesters? The main byproduct of bio digesters is biogas, which is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, and other gases.
- How can the slurry produced in bio digesters be used? The slurry produced in bio digesters is rich in nutrients and can be used as a fertilizer for crops, improving soil fertility.
- What are the challenges associated with bio digesters? Some of the key challenges associated with bio digesters include high initial investment costs, technical expertise requirements, and regulatory hurdles.