Waste management has become a major issue in Kenya, as waste generation continues to increase with the growing population and urbanization.
Waste not only poses environmental challenges but also health risks to the community.
While there are various waste management techniques, the use of bio-digesters has emerged as a sustainable solution for waste management in Kenya.
This article will delve into the benefits of bio-digesters, how they work, their impact on the environment, and why they are the future of waste management in Kenya.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Waste management has become a critical issue globally, with governments and organizations focusing on reducing waste generation and improving waste management practices.
Kenya, like other developing countries, faces numerous challenges in managing waste due to limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and a growing population.
Consequently, improper waste disposal has led to environmental degradation, health hazards, and poor sanitation.
However, with advancements in technology, there are sustainable waste management techniques that can help mitigate these challenges, including the use of bio-digesters.
The problem with traditional waste management methods in Kenya
Kenya has traditionally relied on open dumping and burning of waste, which have adverse environmental effects.
Open dumping results in the accumulation of waste, creating breeding grounds for pests and diseases, and emitting greenhouse gases.
Similarly, burning waste produces toxic gases and carcinogens that pollute the air and increase the risk of respiratory diseases.
Additionally, most of the waste is non-biodegradable, making it difficult to dispose of effectively, leading to the accumulation of waste in landfills.
What are Bio-Digesters and how do they work?
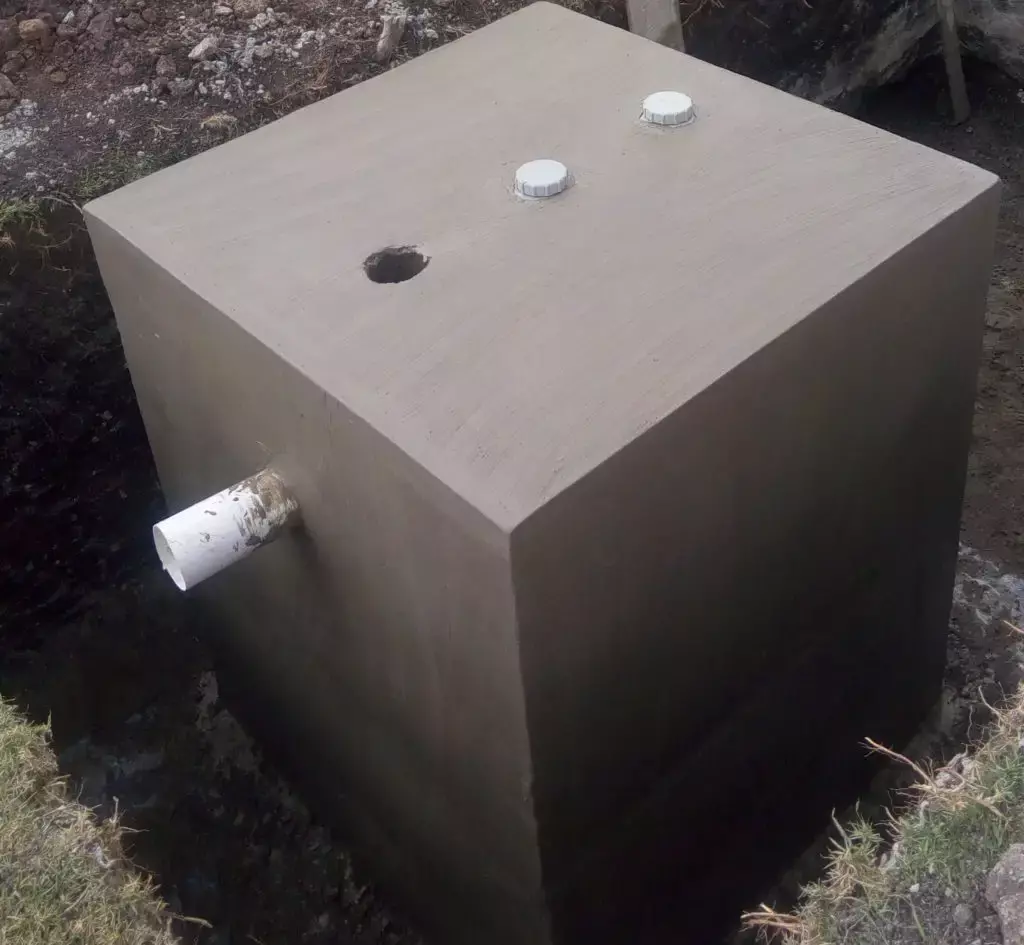
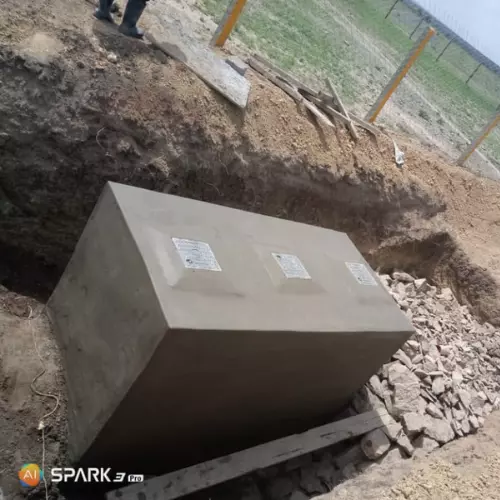
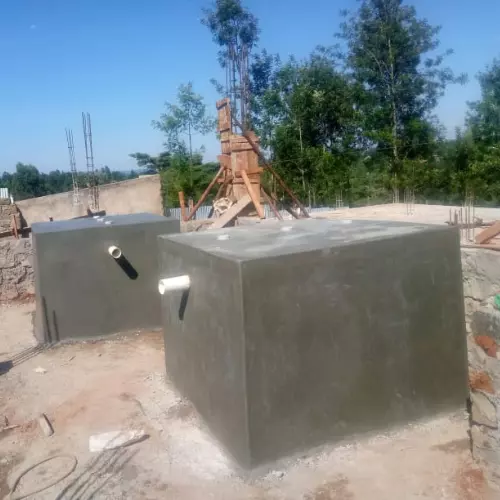
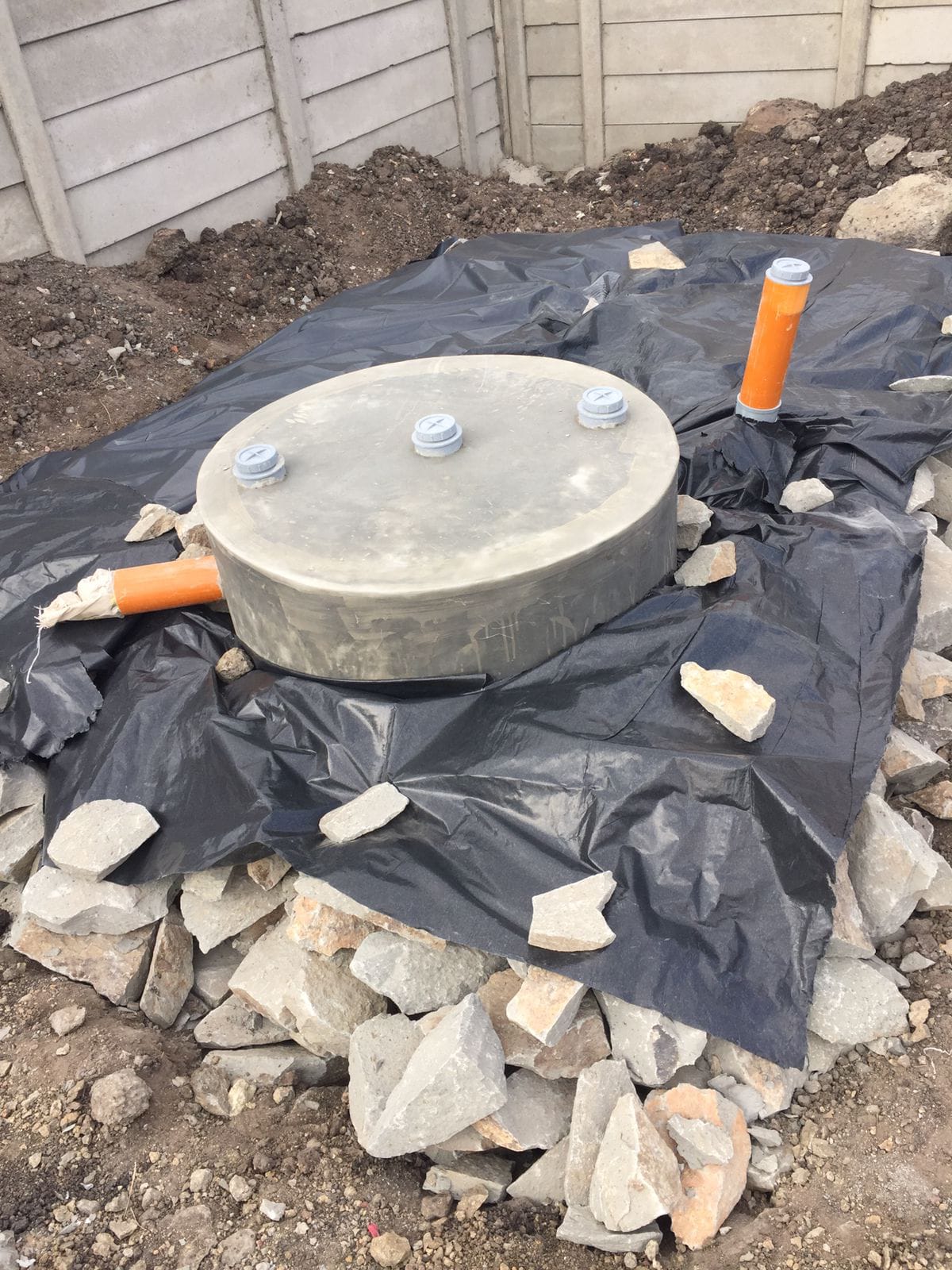
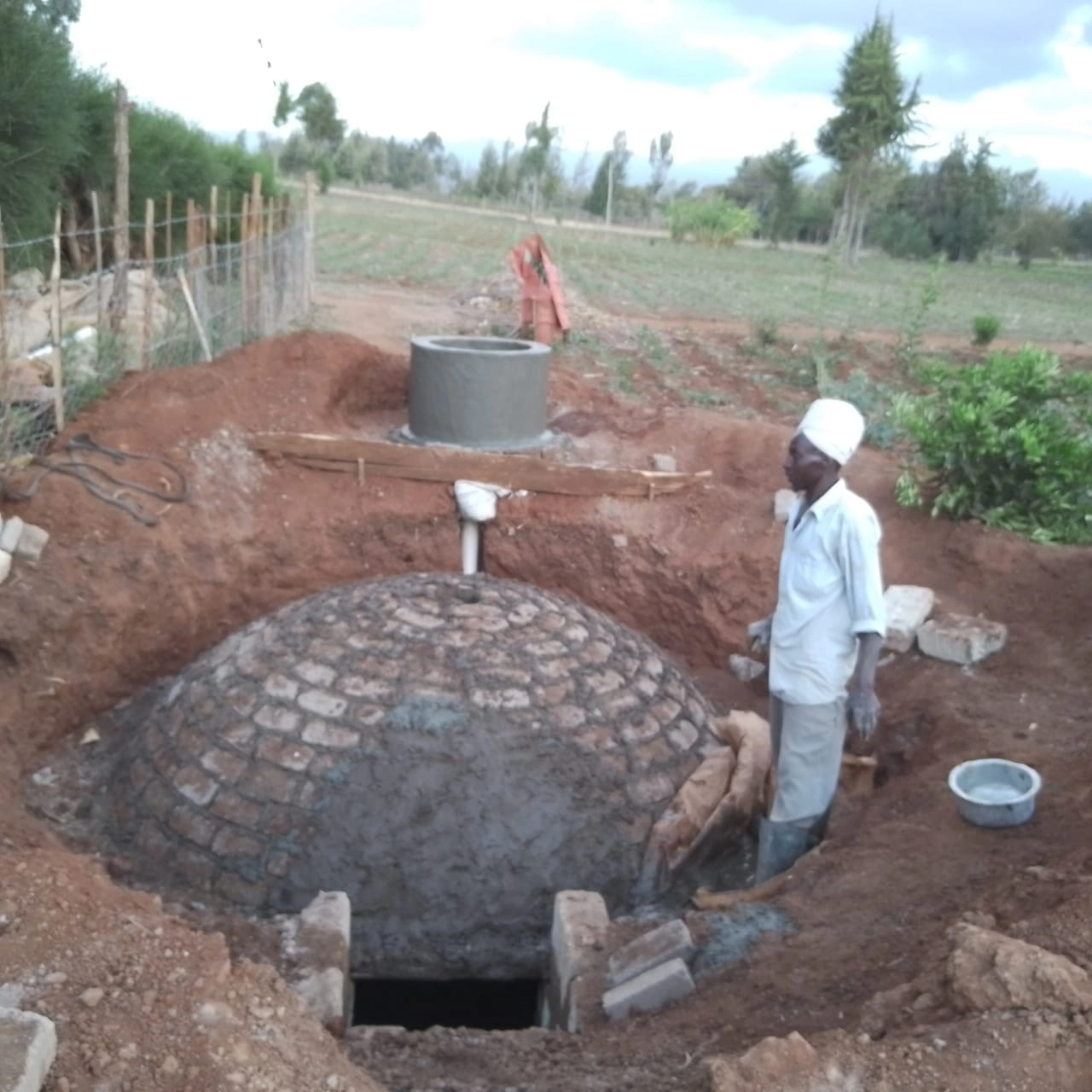
Bio-digesters are systems that use natural processes to break down organic waste into biogas and biofertilizer.
The process involves placing organic waste into a sealed container, where bacteria break down the waste, producing biogas that can be used for cooking or electricity and biofertilizer for agriculture.
Bio-digesters can be designed for household or industrial use, depending on the scale of waste generation.
The benefits of Bio-Digesters
Bio-digesters have numerous benefits, including:
a) Reduction of waste
Bio-digesters help reduce waste by breaking down organic waste, which constitutes a significant percentage of waste generated. This reduction in waste leads to a decrease in the amount of waste sent to landfills, reducing environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
b) Biogas production
Bio-digesters produce biogas, which is a clean and renewable source of energy. Biogas can be used for cooking, heating, and lighting, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and reducing household expenses.
c) Biofertilizer production
Bio-digesters produce biofertilizer, which is rich in nutrients and can be used to improve soil fertility, leading to increased crop yields and agricultural productivity.
d) Cost-effective
Bio-digesters are cost-effective, as they reduce waste disposal costs and provide a source of energy and fertilizer for households and businesses.
Bio-Digesters and the Environment
Bio-digesters have a positive impact on the environment, as they reduce greenhouse gas emissions, minimize waste generation, and promote sustainable practices.
Bio-digesters help reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, reducing environmental pollution, and minimizing the impact of waste on soil and water resources.
The Future of Waste Management in Kenya
The future of waste management in Kenya lies in sustainable practices that promote environmental conservation and improve public health.
Bio-digesters have emerged as a viable solution to the waste management challenges in Kenya, with various organizations and the government promoting their adoption.
The Kenyan government has made significant strides in promoting bio-digesters through tax incentives and subsidies for households and businesses that install bio-digesters.
Additionally, various organizations have partnered with local communities to install bio-digesters in households and schools, promoting sustainable waste management practices.
Bio-digesters have immense potential in Kenya, given the country’s high rate of agricultural and food waste.
Bio-digesters can help convert waste into a valuable resource, reducing waste pollution, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Furthermore, the production of biogas can help reduce the dependence on fossil fuels, reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the adoption of bio-digesters has significant benefits for waste management in Kenya.
Bio-digesters help reduce waste, produce renewable energy and fertilizer, and promote sustainable waste management practices.
With the Kenyan government and various organizations promoting the adoption of bio-digesters, the future of waste management in Kenya looks promising.
-
BioDigester 3M³
Rated 5.00 out of 5KSh 230,000 Order Via WhatsApp -
Sale!
BioDigester 4M³
Rated 5.00 out of 5KSh 280,000Original price was: KSh 280,000.KSh 260,000Current price is: KSh 260,000. Order Via WhatsApp -
Sale!
BioDigester 2M³
KSh 160,000Original price was: KSh 160,000.KSh 130,000Current price is: KSh 130,000. Order Via WhatsApp -
Sale!
BioDigester 1M³
Rated 5.00 out of 5KSh 85,000Original price was: KSh 85,000.KSh 65,000Current price is: KSh 65,000. Order Via WhatsApp
FAQs
- Are bio-digesters expensive to install?
While the initial cost of installing a bio-digester can be high, it pays off in the long run through reduced waste disposal costs and a source of renewable energy and fertilizer.
- Can bio-digesters handle all types of waste?
Bio-digesters can handle organic waste, including food waste, agricultural waste, and animal waste. However, non-organic waste should be disposed of through appropriate channels.
- Do bio-digesters emit any harmful gases?
Bio-digesters produce biogas, which is a clean and renewable source of energy. However, the handling of biogas should be done carefully to avoid accidents.
- Are there any tax incentives for installing bio-digesters in Kenya?
Yes, the Kenyan government provides tax incentives and subsidies for households and businesses that install bio-digesters.
- Can bio-digesters be used in urban areas?
Yes, bio-digesters can be used in urban areas, with designs that suit the scale of waste generation. They can be installed in households, schools, and commercial buildings, promoting sustainable waste management practices in urban areas.