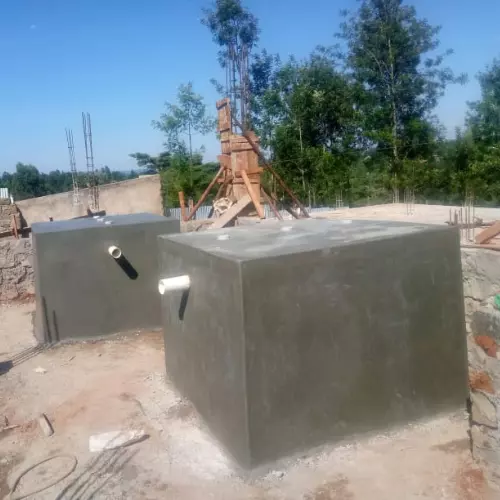
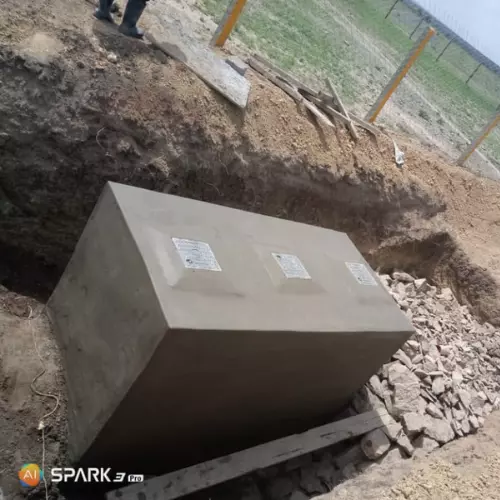
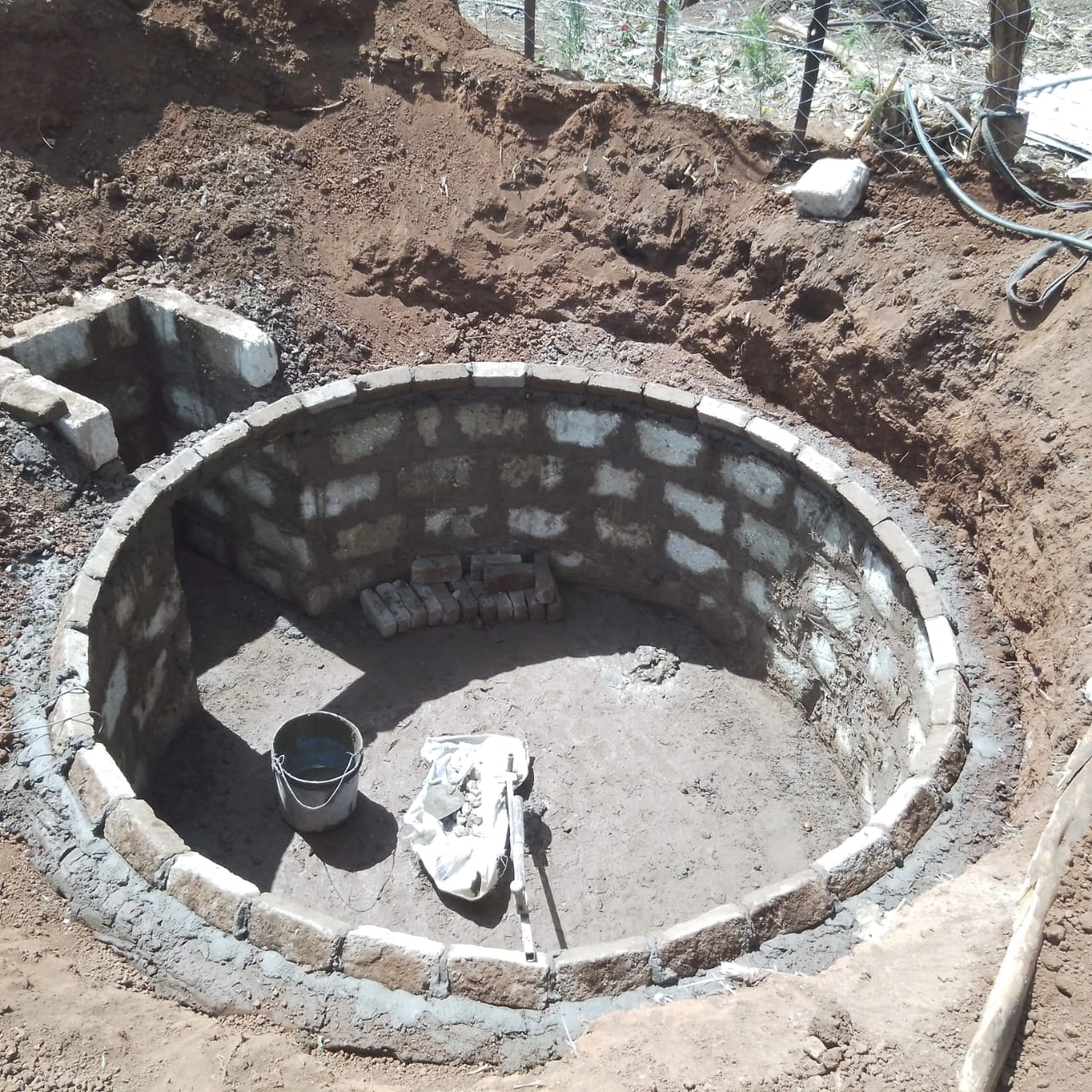
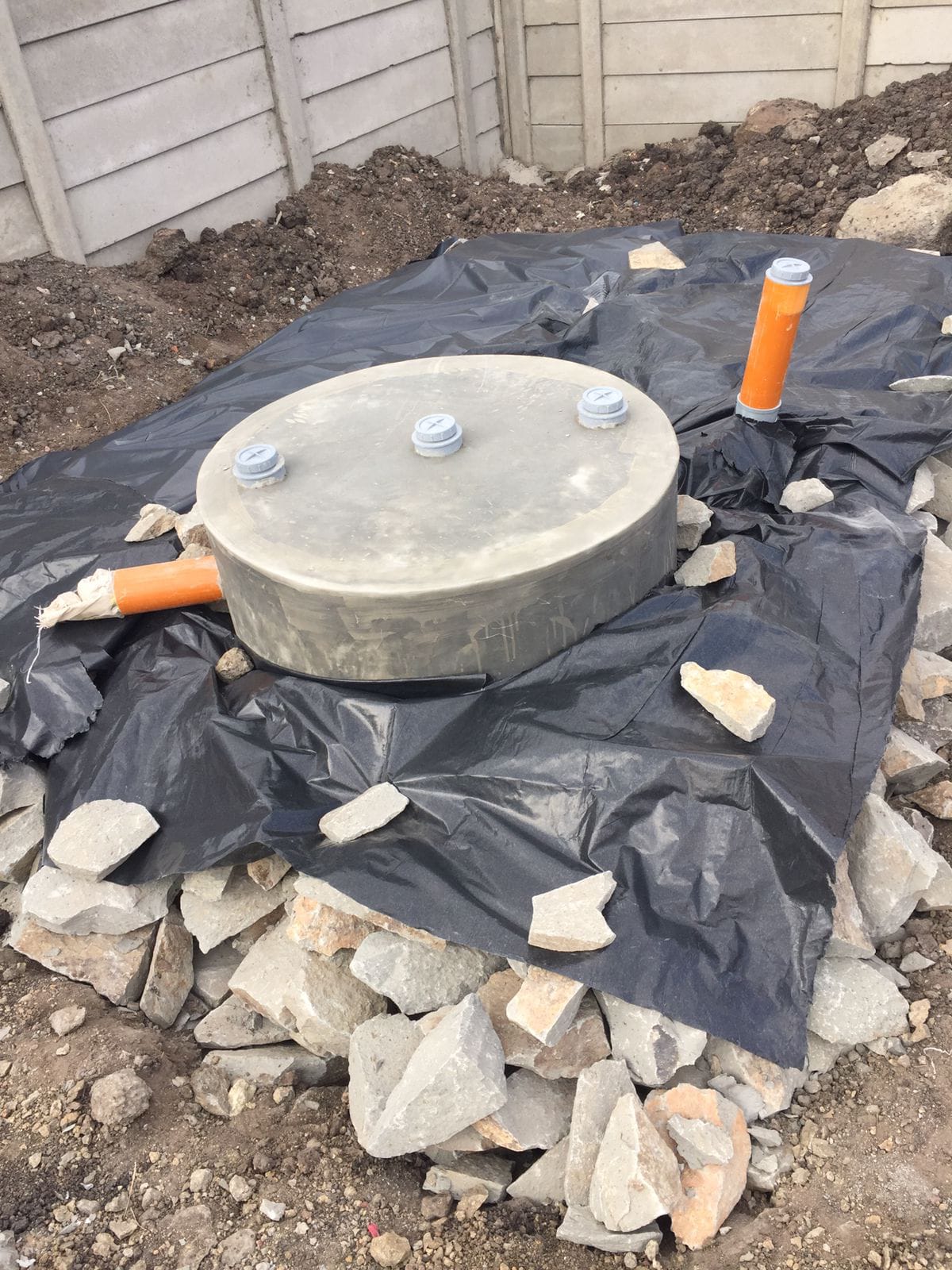
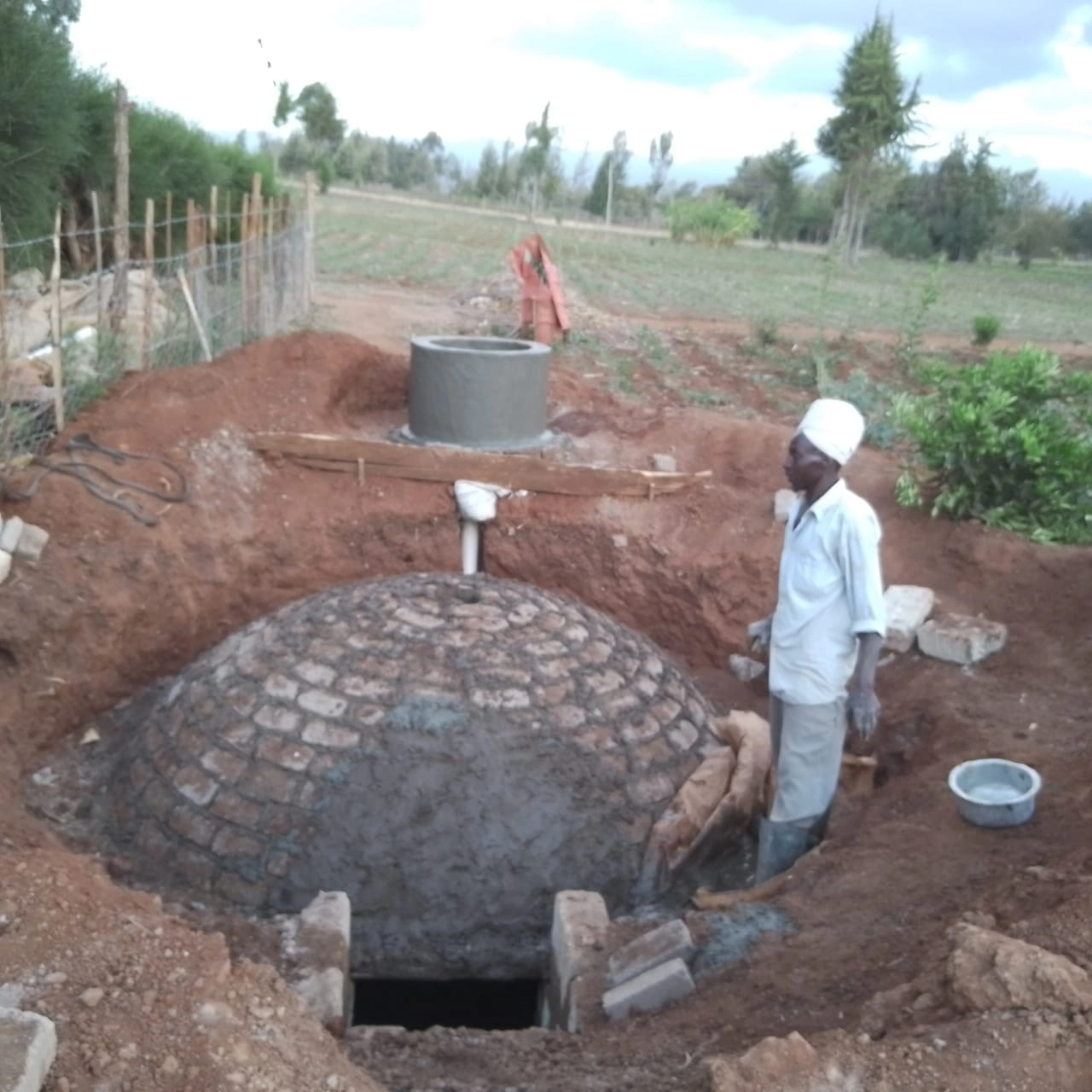
Human waste management is a crucial aspect of maintaining public health and preserving the environment. In recent years, the use of biodigesters as a human waste management system has become increasingly popular.
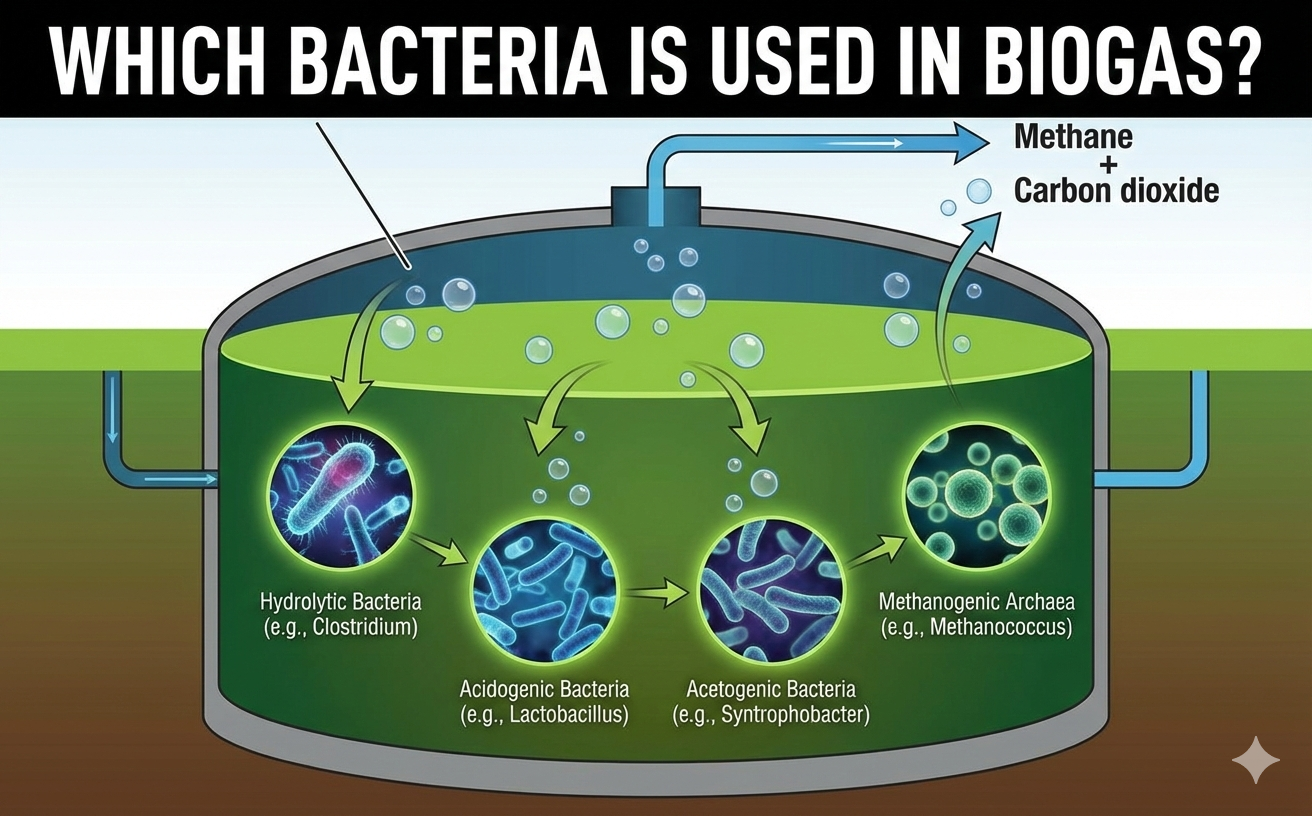
Biodigesters are systems that use microorganisms to break down organic waste, producing biogas and nutrient-rich effluent.
In this article, we will explore how biodigesters work and the benefits and challenges associated with using them.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Human waste management is a critical issue in today’s world, with increasing population growth and urbanization leading to greater volumes of waste produced.
The disposal of this waste poses significant challenges, including environmental pollution, health hazards, and economic costs.
Biodigesters are a sustainable and efficient solution to these challenges, offering a way to treat human waste while producing useful byproducts such as biogas and nutrient-rich effluent.
By understanding how biodigesters work as a human waste management system, we can contribute to a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.
Types of BioDigesters
There are two main types of biodigesters: anaerobic and aerobic digesters.
Anaerobic digesters operate in an oxygen-free environment, while aerobic digesters require oxygen to function.
How BioDigesters Work
Anaerobic Digesters
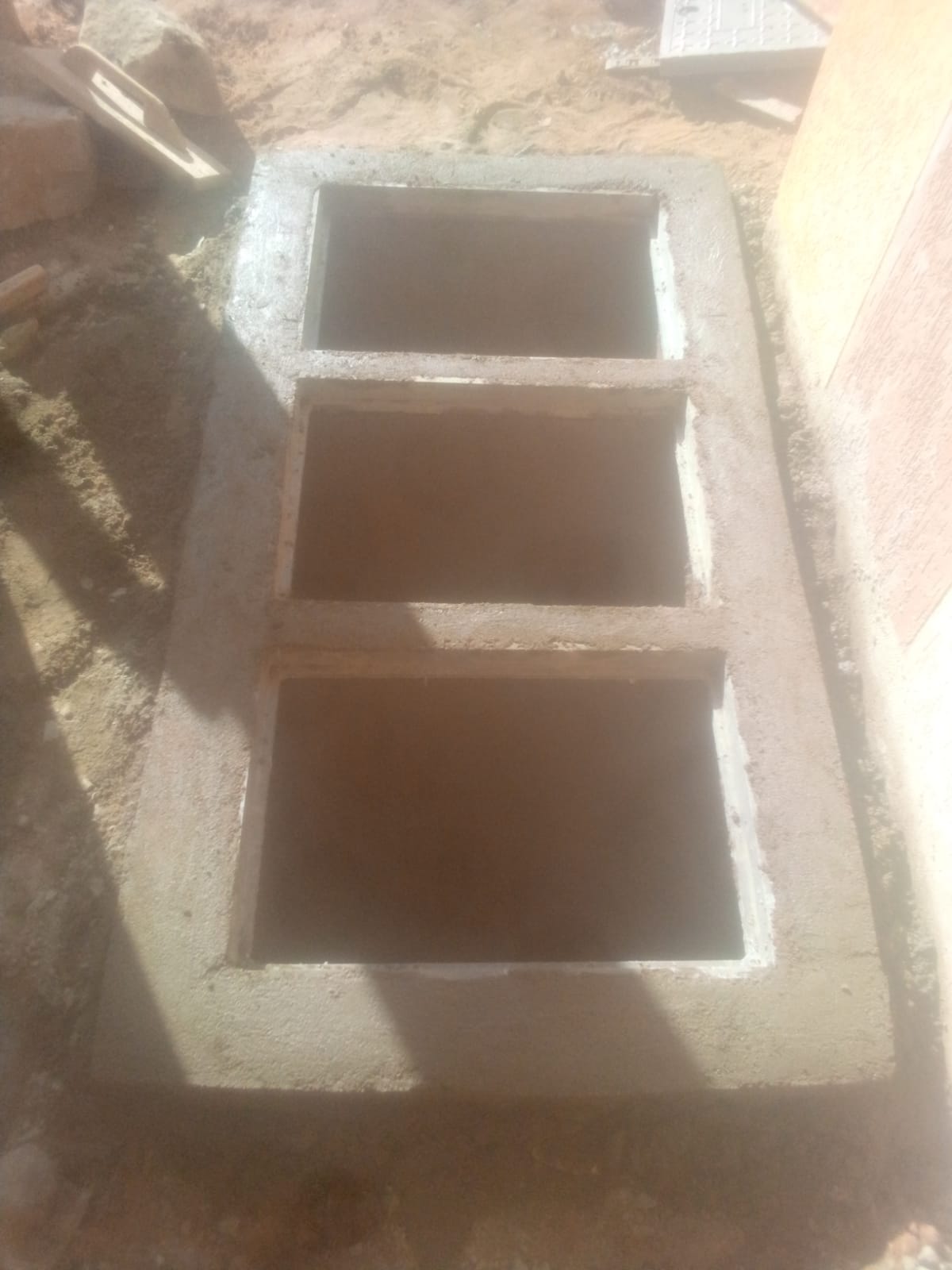
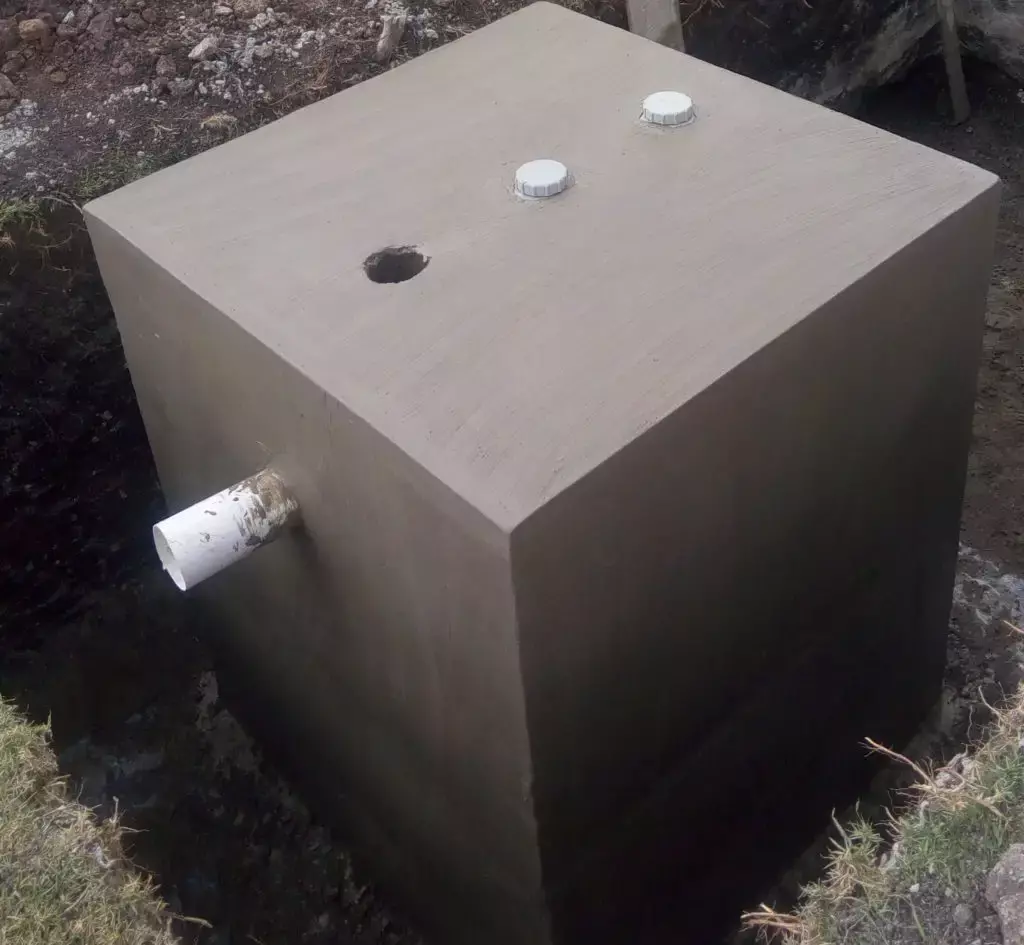
Anaerobic digesters use a natural biological process to break down organic waste. The waste is first collected and pumped into the digester, where it is heated and agitated.
The microorganisms in the digester consume the waste and produce biogas as a byproduct. The biogas can be used as a source of energy, while the effluent can be used as a fertilizer.
Anaerobic digesters have several advantages over other waste management systems.
They produce renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize the need for chemical fertilizers.
However, they also have some disadvantages, such as requiring a large amount of space and expertise to operate.
Anaerobic digesters are commonly used in agriculture, food processing, and wastewater treatment plants.
Aerobic Digesters
Aerobic digesters use oxygen to break down organic waste. The waste is first collected and mixed with air, and then placed in the digester.
The microorganisms in the digester consume the waste and produce carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. The effluent can be used as a fertilizer.
Aerobic digesters have several advantages over anaerobic digesters. They require less space, produce less odor, and are easier to operate.
However, they also have some disadvantages, such as requiring more energy to operate and producing less biogas.
Aerobic digesters are commonly used in urban areas and smaller communities.

Benefits of Using Bio Digesters
There are several benefits to using biodigesters as a human waste management system.
One of the main benefits is environmental sustainability. Biodigesters produce renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize the need for chemical fertilizers.
Additionally, biodigesters can help prevent pollution of water sources and reduce the spread of disease. Another benefit of using biodigesters is economic efficiency.
Biodigesters can generate income through the sale of biogas and effluent as fertilizer. This can provide an additional source of revenue for farmers and other businesses.
Biodigesters also have social benefits. They can provide access to clean energy and sanitation in rural areas, improving the quality of life for communities. Additionally, the use of biodigesters can create jobs and stimulate economic development.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a BioDigester
When choosing a biodigester, several factors should be considered.
These include the size of the system, operating costs, maintenance requirements, and location and climate.
The size of the system should be appropriate for the amount of waste being produced.
Smaller systems may be suitable for households, while larger systems may be necessary for commercial or industrial applications.
Operating costs can vary depending on the type of system and the amount of waste being processed.
Anaerobic digesters generally require more maintenance and expertise, which can increase operating costs.
The location and climate can also affect the performance of a biodigester.
The system should be located in an area with sufficient space, access to water, and appropriate temperature and humidity conditions.
Challenges Faced When Using BioDigesters
While biodigesters offer many benefits, there are also some challenges associated with their use.
These include technical challenges and social and cultural challenges.
Technical challenges can include issues with system design, maintenance, and operation.
Improperly designed or maintained systems can result in decreased efficiency and increased costs.
Social and cultural challenges can include issues related to acceptance and adoption of the technology.
Some communities may be resistant to the use of biodigesters due to cultural or religious beliefs.
Additionally, lack of awareness and understanding of the technology can hinder adoption.
This is why you need proffesionals to help you design, build and maintain your BioDigester. Bio Digester Kenya is a team of proffesionals who specialise in designing, installing and maintaining BioDigesters.
We will help you choose the right BioDigester for your use case. We will also help you activate your BioDigester using our quality Bacteria. Get in touch with us today to start your BioDigester Journey.
Conclusion
Biodigesters are a sustainable and efficient solution for human waste management.
They offer many benefits, including environmental sustainability, economic efficiency, and social benefits.
However, several factors should be considered when choosing a biodigester, and there may be challenges associated with its use.
Nonetheless, the importance of adopting biodigesters as a human waste management system cannot be overstated.
FAQs
What is a bio digester? A bio digester is a system that uses microorganisms to break down organic waste, producing biogas and nutrient-rich effluent.
How do bio digesters work? Bio digesters work by collecting organic waste and pumping it into a digester, where it is broken down by microorganisms. The byproducts of this process are biogas and effluent.
What are the benefits of using bio digesters? Bio digesters offer several benefits, including environmental sustainability, economic efficiency, and social benefits. They can generate renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and provide access to clean energy and sanitation in rural areas.
What factors should be considered when choosing a bio digester? When choosing a bio digester, factors such as system size, operating costs, maintenance requirements, and location and climate should be considered.
What challenges are faced when using bio digesters? Challenges associated with the use of bio digesters can include technical challenges related to system design, maintenance, and operation, as well as social and cultural challenges related to acceptance and adoption of the technology.