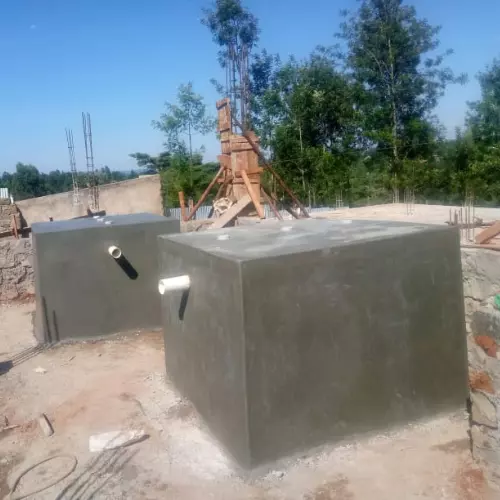
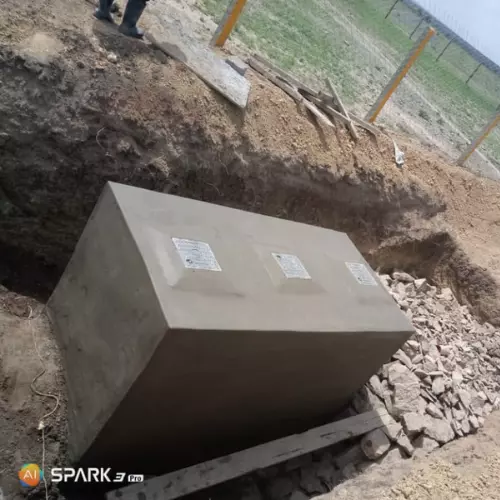
In recent years, the concept of home biodigesters have gained traction as an eco-friendly and sustainable solution for managing organic waste.
With growing concerns about environmental pollution and the need for renewable energy sources, many homeowners are turning to biodigesters as a viable alternative to conventional waste management systems.
In this article, we’ll explore the design, benefits, and installation process of home biodigesters, shedding light on how these innovative systems can revolutionize waste management in residential settings.
Table of Contents
Understanding Biodigesters
What is a Biodigester?
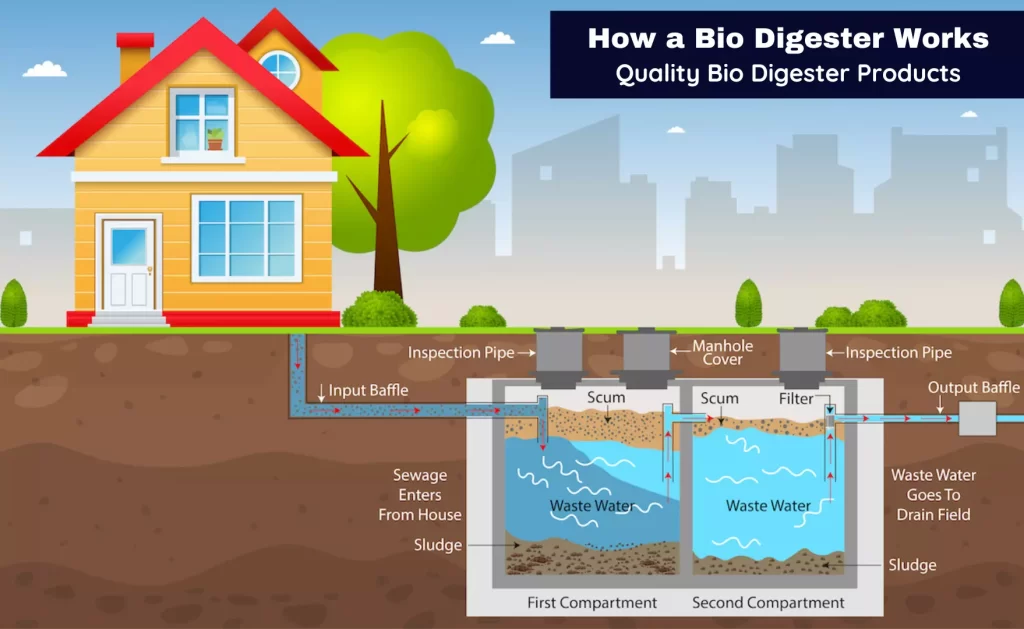
A biodigester is a biological waste management system that harnesses anaerobic digestion to break down organic matter into biogas and nutrient-rich effluent.
Unlike traditional septic tanks, which rely on passive filtration, biodigesters use microorganisms to facilitate the decomposition process, resulting in the production of renewable energy and organic fertilizer.
How Do Biodigesters Work?
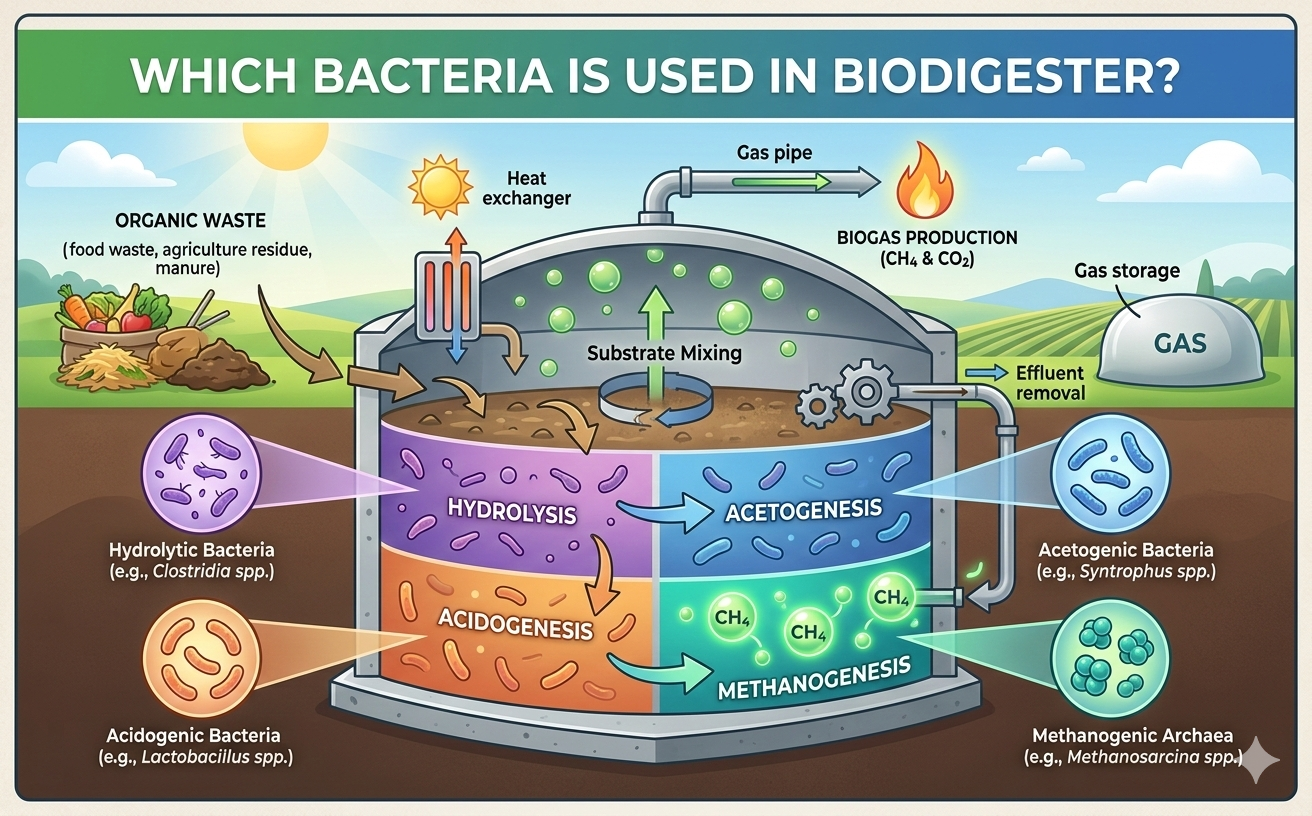
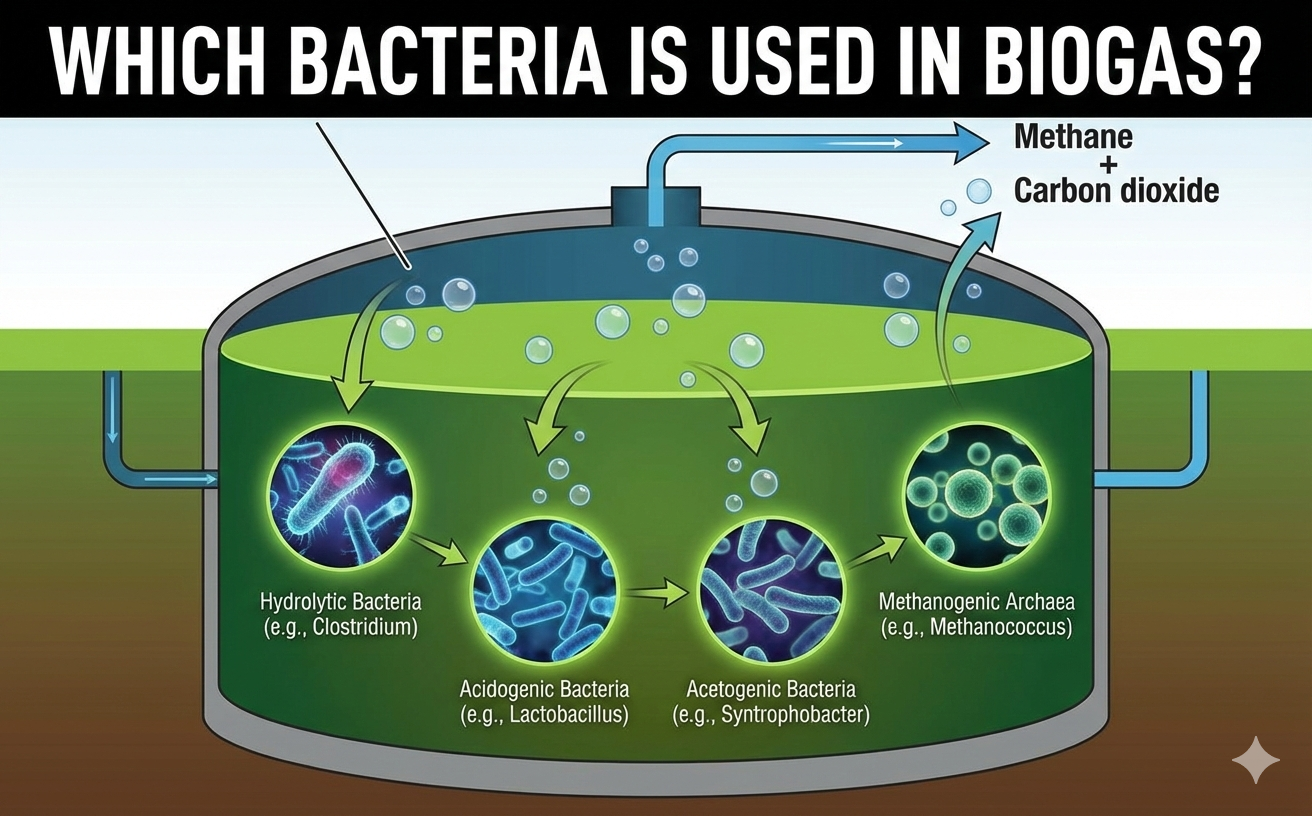
Biodigesters operate through a series of biological and chemical processes.
Microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, break down organic waste material in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas and digestate.
Biogas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide, can be captured and used for cooking, heating, or electricity generation, while the digestate can be used as fertilizer for agricultural purposes.
Benefits of Home Biodigesters
Environmental Sustainability
One of the key benefits of home biodigesters is their contribution to environmental sustainability.
By converting organic waste into biogas and fertilizer, biodigesters help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, minimize reliance on fossil fuels, and promote soil health through nutrient recycling.
Cost Savings
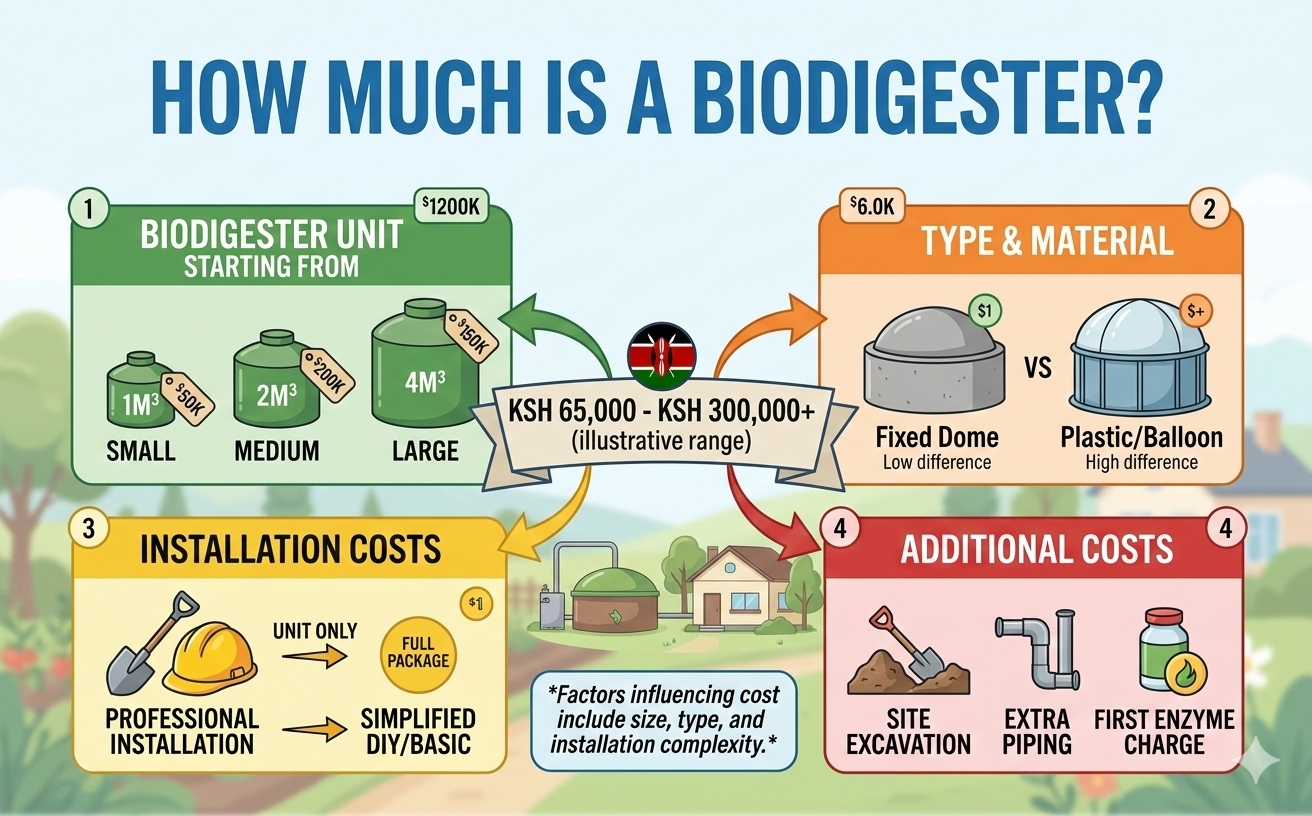
In addition to their environmental benefits, home biodigesters offer significant cost savings over time.
While the initial investment may seem daunting, the long-term savings on energy bills, waste disposal fees, and fertilizer purchases can make biodigesters a wise financial investment for homeowners.
Waste Reduction
Home biodigesters also help reduce the volume of organic waste sent to landfills or incinerators, thereby mitigating pollution and conserving valuable landfill space.
By recycling organic waste on-site, homeowners can minimize their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Design Considerations
Size and Capacity
When designing a home biodigester, it is essential to consider the size and capacity required to meet the household’s waste generation needs.
Factors such as the number of occupants, daily waste production, and available space will influence the size of the biodigester tank and the efficiency of the system.
Location
The location of the biodigester is another critical consideration. Ideally, the biodigester should be installed in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
Additionally, it should be easily accessible for maintenance and monitoring purposes.
Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for biodigester construction is essential to ensure durability and longevity.
Common materials include high-density polyethylene (HDPE) tanks, PVC pipes, and stainless steel fittings, which are resistant to corrosion and degradation.
Installation Process
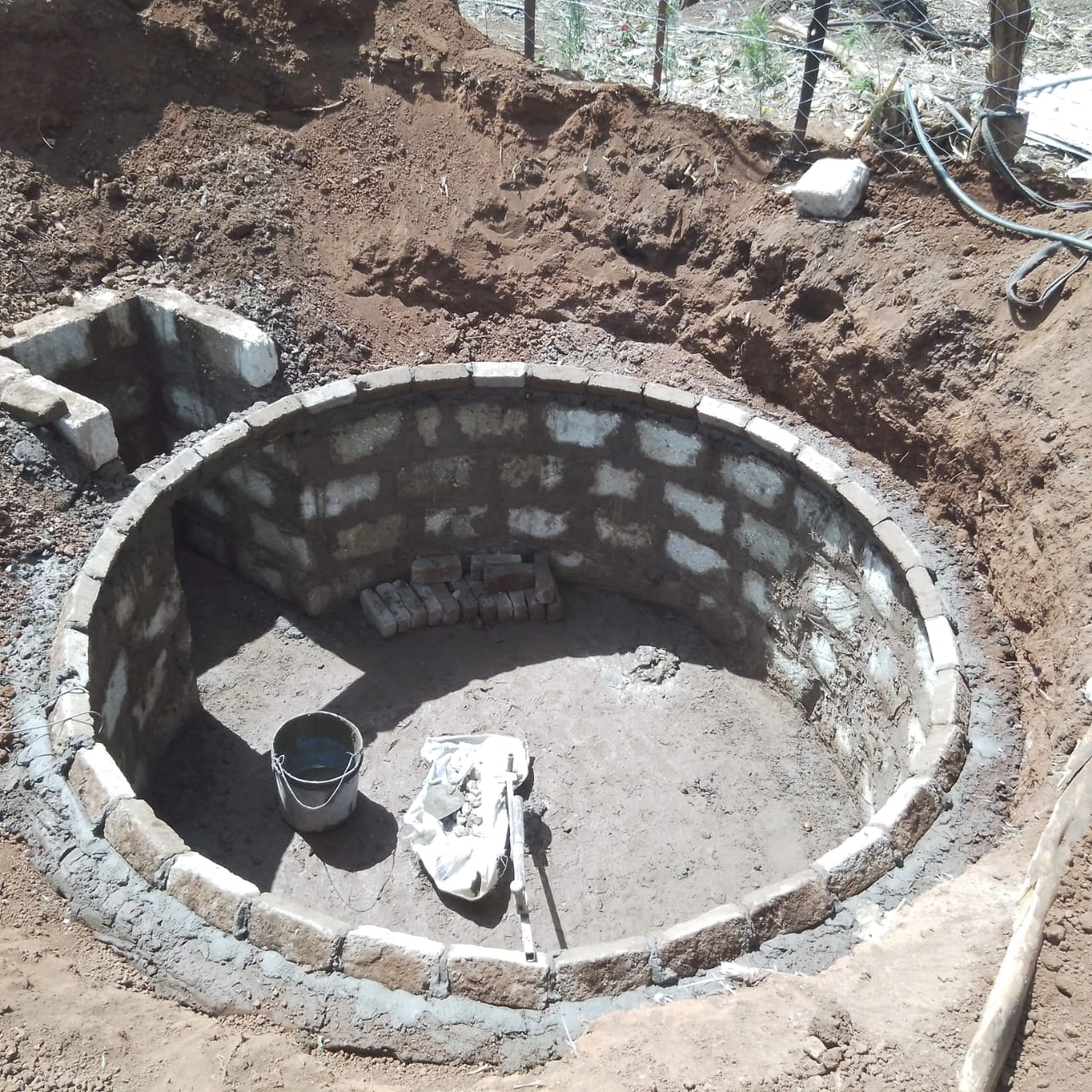
Site Preparation
Before installing a home biodigester, proper site preparation is necessary. This may involve excavating a pit or trench, compacting the soil, and creating a stable foundation for the biodigester tank.
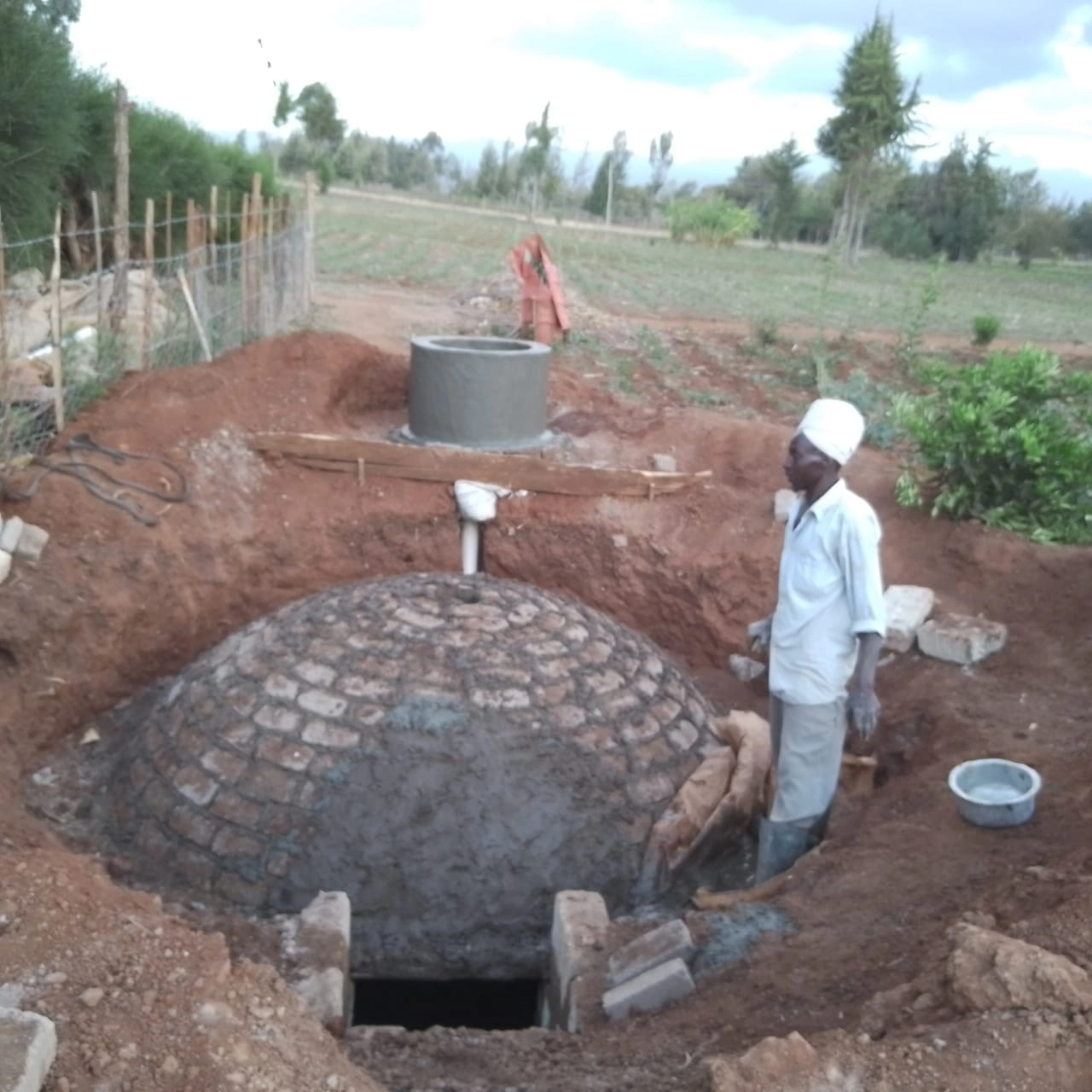
Tank Installation
Once the site is prepared, the biodigester tank can be installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Care should be taken to ensure proper alignment and levelness to prevent leaks and structural issues.
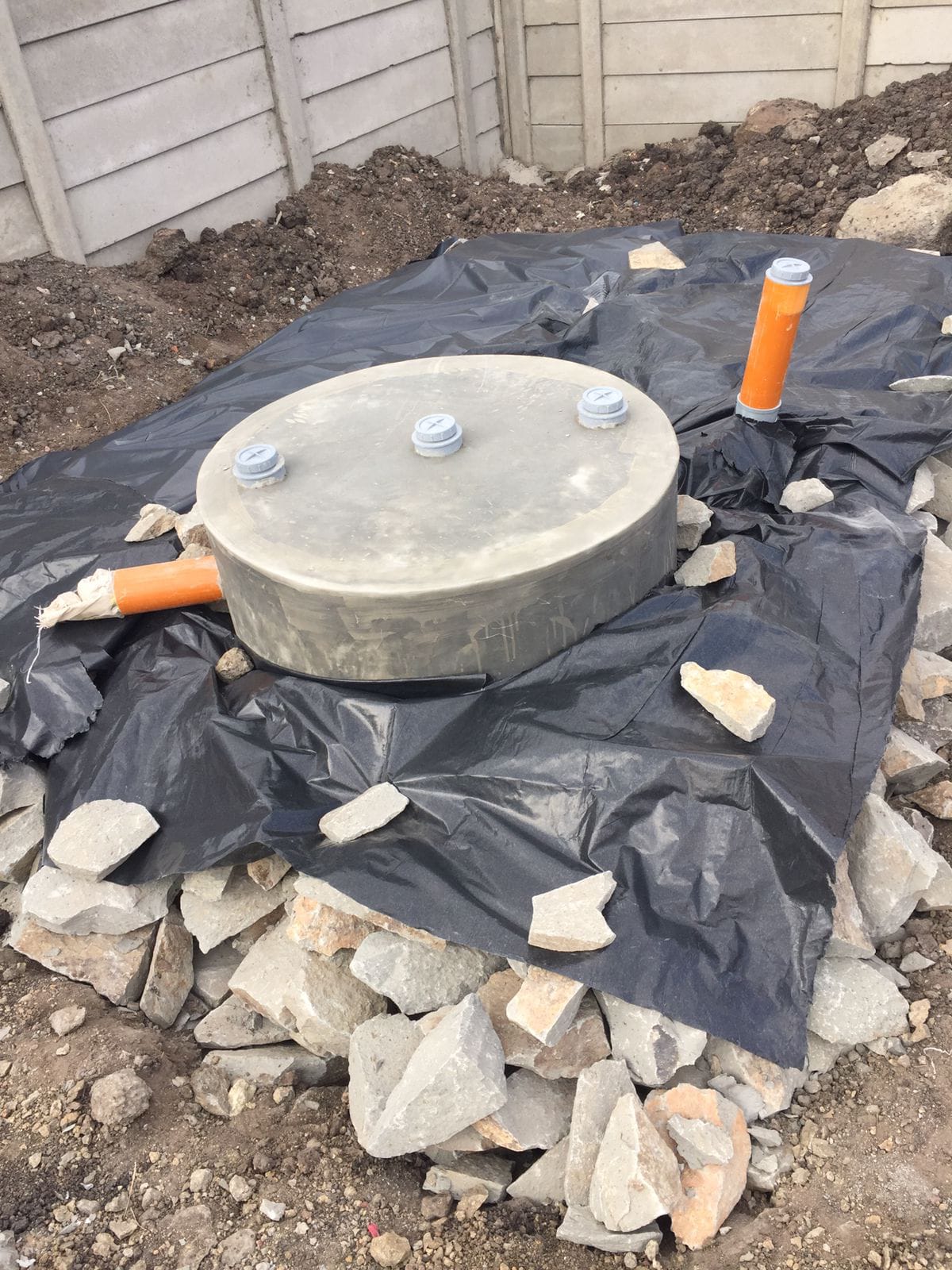
Plumbing Connections
After the tank is in place, the plumbing connections can be made to facilitate the flow of waste into the biodigester and the removal of biogas and digestate.
It is essential to use high-quality pipes and fittings to prevent leaks and ensure efficient operation.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular Inspections
While home biodigesters require minimal maintenance compared to traditional waste management systems, regular inspections are essential to ensure optimal performance.
This includes visually inspecting the tank and plumbing for signs of damage or wear, checking gas production levels, and monitoring the quality of the effluent.
Waste Management
Proper waste management practices are crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of a home biodigester.
This involves segregating organic waste from non-biodegradable materials, ensuring a balanced diet of inputs for the microorganisms, and avoiding toxic or harmful substances that can disrupt the digestion process.
Gas Production Monitoring
Monitoring gas production is an essential part of biodigester maintenance, as it allows homeowners to gauge the system’s performance and efficiency.
By tracking gas production levels over time, adjustments can be made to optimize operating conditions and maximize biogas yields.
Applications in Residential Homes
Waste Management
The primary application of home biodigesters is organic waste management, including kitchen scraps, food leftovers, garden trimmings, and animal waste.
By diverting organic waste from landfills, biodigesters help reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable waste management practices.
Cooking and Heating
Biogas produced by home biodigesters can be used as a clean and renewable energy source for cooking, heating, and other household applications.
Biogas stoves, water heaters, and space heaters are commonly fueled by biogas, providing an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, home biodigesters offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for organic waste management in residential settings.
By harnessing the power of anaerobic digestion, these innovative systems convert organic waste into biogas and nutrient-rich fertilizer, reducing environmental impact and promoting energy independence.
With proper design, installation, and maintenance, home biodigesters can revolutionize waste management practices and contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the lifespan of a home biodigester?
- The lifespan of a home biodigester depends on various factors, including the quality of materials, maintenance practices, and operating conditions. With proper care, biodigesters can last upwards of 15-20 years or more.
Can a biodigester handle all types of organic waste?
- While biodigesters can process a wide range of organic waste materials, some may be more suitable than others. Generally, biodigesters can handle kitchen scraps, food waste, animal manure, and plant residues, but certain materials like plastic, metal, and glass should be avoided.
How much space is needed for installing a home biodigester?
- The space required for installing a home biodigester depends on the size and capacity of the system. Small-scale biodigesters may only require a few square meters of space, while larger systems may need several square meters or more.
What are the environmental benefits of using a home biodigester?
- Home biodigesters offer several environmental benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, decreased reliance on landfills, and conservation of natural resources. By converting organic waste into biogas and fertilizer, biodigesters help mitigate climate change and promote sustainable waste management practices.
How often should a home biodigester be serviced?
- Home biodigesters should be serviced regularly to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. This may include annual inspections, cleaning of pipes and filters, and monitoring gas production levels. Additionally, any maintenance issues should be addressed promptly to prevent system failure and prolong the lifespan of the biodigester.